Paper on ORR of Spinels Published in ACS Catalysis
Our team’s latest paper on the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) behavior of MnFe2O4 and Fe3O4 has been published in ACS Catalysis. Led by Alexandria Bredar and Byron Farnum, this study reveals differences in redox behavior that can be uniquely examined using model thin-film oxide systems.
From the abstract:
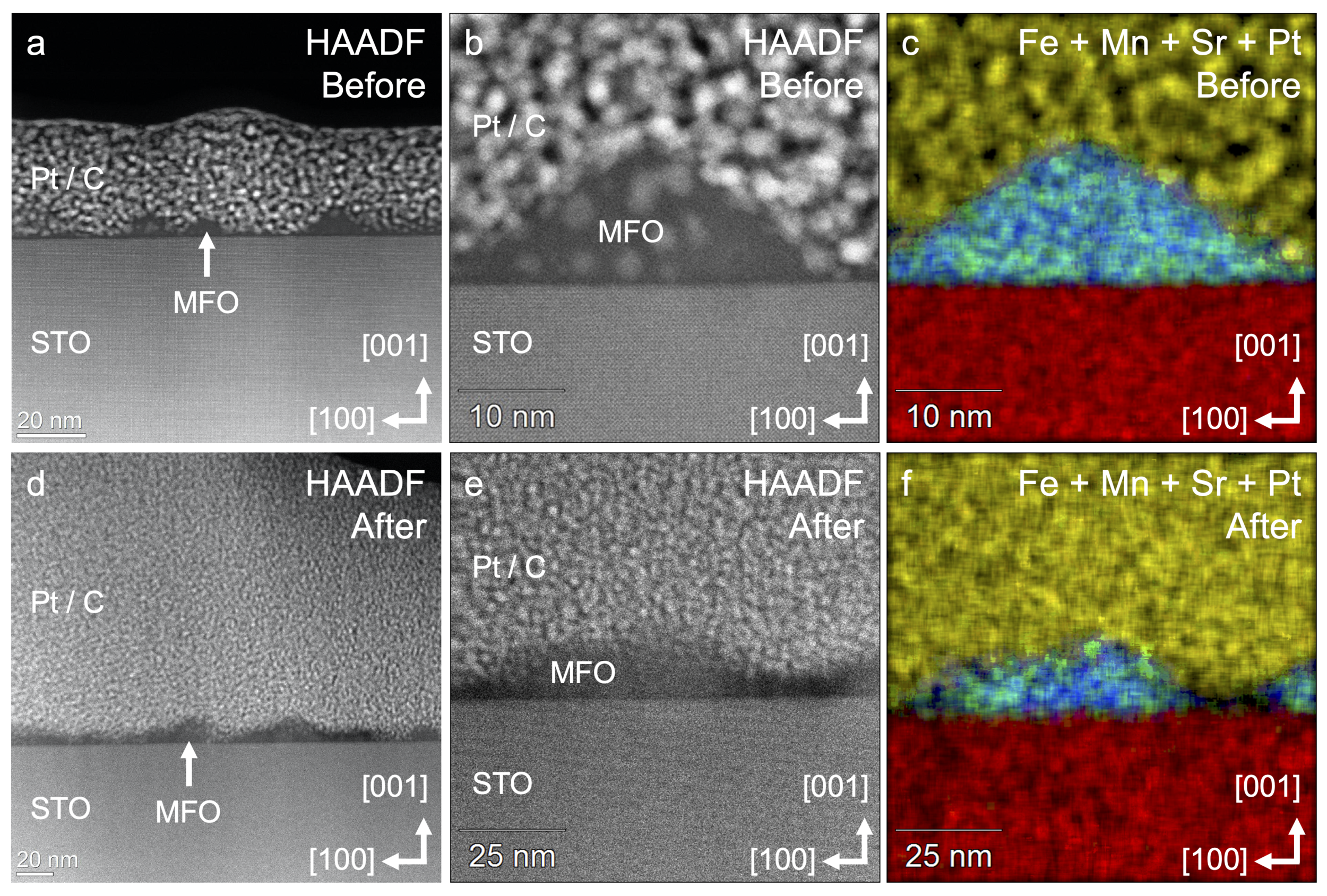
Nanocrystalline MnFe2O4 has shown promise as a catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in alkaline solutions, but the material has been sparingly studied as highly ordered thin-film catalysts. To examine the role of surface termination and Mn and Fe site occupancy, epitaxial MnFe2O4 and Fe3O4 spinel oxide films were grown on (001)- and (111)-oriented Nb:SrTiO3 perovskite substrates using molecular beam epitaxy and studied as electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). High-resolution X-ray diffraction (HRXRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) show the synthesis of pure phase materials, while scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) and reflection high-energy electron diffraction (RHEED) analysis demonstrate island-like growth of (111) surface-terminated pyramids on both (001)- and (111)-oriented substrates, consistent with the literature and attributed to the lattice mismatch between the spinel films and the perovskite substrate. Cyclic voltammograms under a N2 atmosphere revealed distinct redox features for Mn and Fe surface termination based on comparison of MnFe2O4 and Fe3O4. Under an O2 atmosphere, electrocatalytic reduction of oxygen was observed at both Mn and Fe redox features; however, a diffusion-limited current was only achieved at potentials consistent with Fe reduction. This result contrasts with that of nanocrystalline MnFe2O4 reported in the literature where the diffusion-limited current is achieved with Mn-based catalysis. This difference is attributed to a low density of Mn surface termination, as determined by the integration of current from CVs collected under N2, in addition to low conductivity through the MnFe2O4 film due to the degree of inversion. Such low densities are attributed to the synthetic method and island-like growth pattern and highlight challenges in studying ORR catalysis with single-crystal spinel materials.
To view the manuscript, visit: https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c05172
To download the article directly, click here.